Table Of Content
Together, the Senate and the House of Representatives provide a balance between the representation of states and the representation of the population. This balance is fundamental to the functioning of the United States government and helps to ensure that both the interests of states and the interests of the people are taken into account when making decisions that affect the country as a whole. This dual legislative structure ensures that no one branch of government becomes too powerful. Whether working on Capitol Hill or in his / her congressional district, a representative’s schedule is extremely busy. Often beginning early in the morning with topical briefings, most representatives move quickly among caucus and committee meetings and hearings. They vote on bills, speak with constituents and other groups, and review constituent mail, press clips and various reports.
Step 2: The bill is debated and put to a vote
Congress also has the power to raise revenue through taxes and to coin money, which helps to ensure the stability of the economy and provide the government with the resources it needs to carry out its responsibilities. Congress is the bicameral legislature that writes the laws for the nation. It is made up of the House of Representatives which has 435 members and the Senate which has 100 members. Or the Democrat's June 2016 filibuster as a protest at the lack of progress on gun control legislation. The House, the only elected chamber at the time, more influence over taxation than the Senate. This power is not very significant today as all House decisions still have to be accepted by the Senate, which can amend or reject House decisions.
Resources on House of Representatives roles and responsibilities
Senators can use this to filibuster bills under consideration, a procedure by which a Senator delays a vote on a bill — and by extension its passage — by refusing to stand down. A supermajority of 60 Senators can break a filibuster by invoking cloture, or the cession of debate on the bill, and forcing a vote. After both chambers accept the bill, joint committees work out the differences between the two versions.
What's a Select Committee?
The number of congressional districts within a state is determined by a census that is conducted every ten years. This census helps to ensure that each district is equal in population and that the voices of citizens are heard in the legislative process. The House of Representatives, on the other hand, is designed to represent the population of the country. Members of the House are elected based on the population of their districts, with larger districts having more representatives than smaller ones. The number of representatives for each state is determined by a census taken every ten years. The idea behind this is to ensure that the voices of citizens from larger populated areas are heard in the legislative process, as they make up a larger portion of the overall population.
The Rules Committee controls what bills go to the House Floor and the terms of debate. Article 1, Section 2 of the Constitution provides for both the minimum and maximum sizes for the House of Representatives. Currently, there are five delegates representing the District of Columbia, the Virgin Islands, Guam, American Samoa, and the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands. The delegates and resident commissioner possess the same powers as other members of the House, except that they may not vote when the House is meeting as the House of Representatives. Congress also maintains an investigative organization, the Government Accountability Office (GAO). Founded in 1921 as the General Accounting Office, its original mission was to audit the budgets and financial statements sent to Congress by the Secretary of the Treasury and the Director of the Office of Management and Budget.
The senators or the members of the Senate are highly qualified and experienced people in their respective domains. One of the major functions of the Senate is its power to try impeachments and removals of the representatives of the House. OBRA 1985 was enacted as a response to the federal budget deficit, which was growing rapidly in the 1980s. The legislation aimed to reduce the deficit by making significant changes to a range of government programs, including reducing spending on social welfare programs and increasing revenue through changes to tax law.
Committees
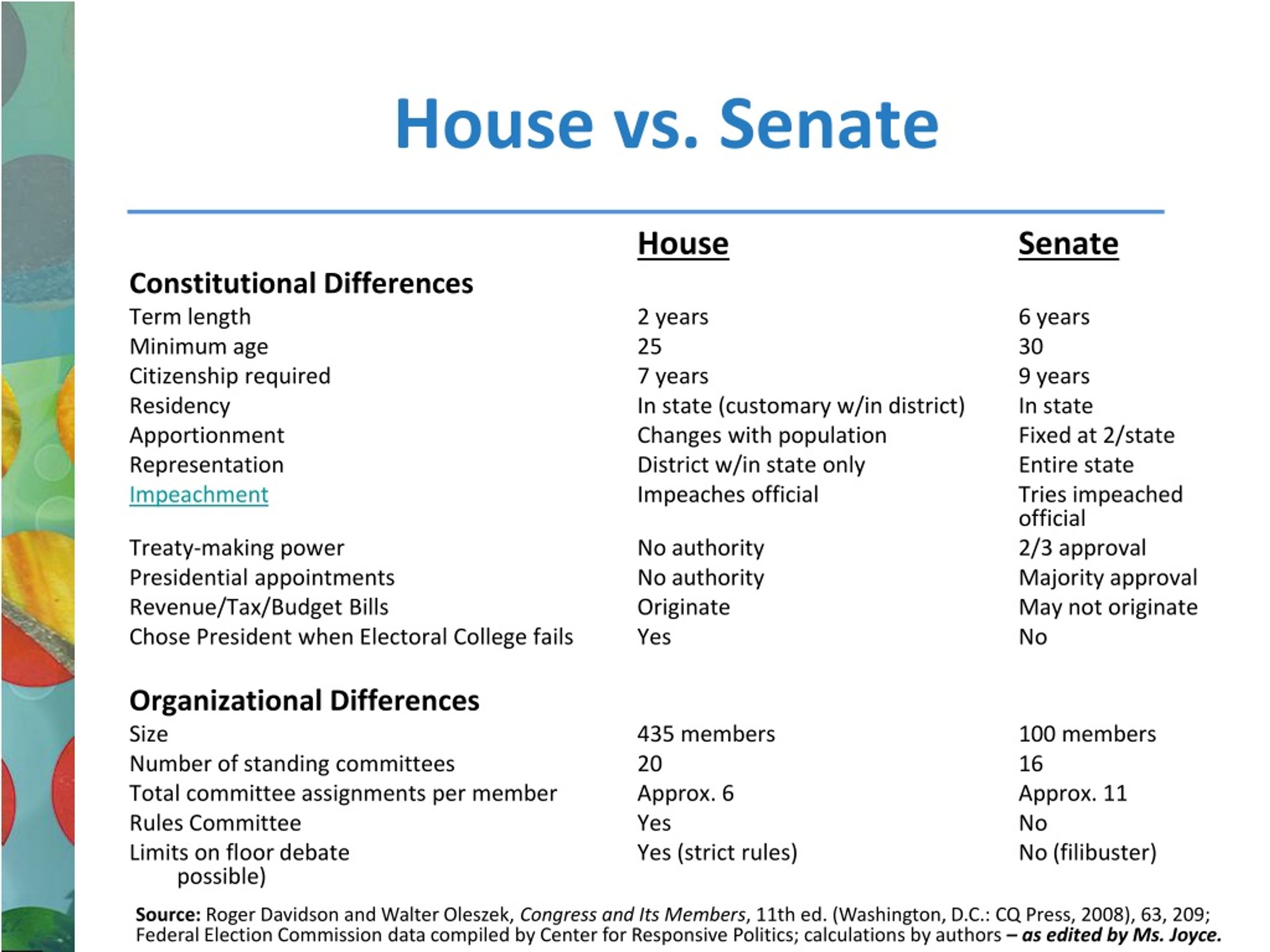
While these chambers are both tasked with making laws, they differ in terms of their size, structure, rules and procedures. This lesson has students first examine the Constitutional foundations of these differences and then explore the ways that these two institutions are currently different. This lesson can be used in a traditional classroom or in a classroom with one-to-one devices.
Article I, Section 2: Composition and Function of the House of Representatives

One of the basic principles of the American workplace is that a hard day’s work deserves a fair day’s pay. A cornerstone of that promise is the Fair Labor Standards Act’s (FLSA) requirement that when most workers work more than 40 hours in a week, they get paid more. The Department of Labor’s new overtime regulation is restoring and extending this promise for millions more lower-paid salaried workers in the U.S. Without controlling one of the houses, Donald Trump is now forced to rely on a Democrat-controlled house to pass his bills and with the current animosity between the two parties, that seems unlikely. The Senate is the upper House of the legislative wing of the US Congress.
Alaska Senate panel approves state spending plan with smaller dividend than House proposed • Alaska Beacon - Alaska Beacon
Alaska Senate panel approves state spending plan with smaller dividend than House proposed • Alaska Beacon.
Posted: Fri, 26 Apr 2024 02:49:41 GMT [source]
The distribution of power within Congress
In this role, the framers expressed their “suspicion of the presidency” by allowing the Senate to serve as a check on executive powers. Senators are empowered to try and judge impeachments; in this capacity, they serve under “oath or affirmation.” In the case of a president’s impeachment, the chief justice of the United States presides. An impeachment conviction requires a two-thirds majority vote of the full Senate.
Overtime protections have been a critical part of the FLSA since 1938 and were established to protect workers from exploitation and to benefit workers, their families and our communities. Strong overtime protections help build America’s middle class and ensure that workers are not overworked and underpaid. This happened in the final two years of Barack Obama's Presidency, when he struggled to make any changes as the Republicans voted down his bills. These are re-elected every two years - in all US elections and midterms. The Democrats took control of the House of Representatives in the Midterms, but the Republicans retained the Senate. The number of members from each state and constituency depends on the intensity of the population of that particular state.
Will the Senate become the House? - ABC News
Will the Senate become the House?.
Posted: Sat, 25 Nov 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
The Constitution grants Congress the sole authority to enact legislation and declare war, the right to confirm or reject many Presidential appointments, and substantial investigative powers. As described above for the House, the Senate’s powers are either enumerated, or expressly stated in the Constitution, or derived from the enumerated powers through the Article I, Section 8 necessary and proper clause. Subsequent rulings have modified these two doctrines, resulting in new categories of powers derived from this constitutional foundation. Noncompliance with a congressional subpoena can carry up to a one-year jail sentence. The case is heard in a judicial forum, and punishment (a sentence) for those found guilty of "contempt of Congress" is handled strictly by the judicial system. The Reapportionment Act of 1929 set the final number of the House at the current 435, with district sizes adjusted according to population growth.
Throughout this stage of the process, the committees and subcommittees call hearings to investigate the merits and flaws of the bill. They invite experts, advocates, and opponents to appear before the committee and provide testimony, and can compel people to appear using subpoena power if necessary. While few constitutional experts and political scholars would argue that the bicameral legislative system works perfectly, most would agree that the formulation has stood the test of time. The president has 10 days to sign or veto bills that Congress sends to the White House for approval.
To bring the bills into alignment, a Conference Committee is convened, consisting of members from both chambers. The members of the committee produce a conference report, intended as the final version of the bill. Depending on where the bill originated, the final text is then enrolled by either the Clerk of the House or the Secretary of the Senate, and presented to the Speaker of the House and the President of the Senate for their signatures. The bicameral legislature that splits legislative duties between a large House of Representatives and a smaller Senate is a key component of the framers’ power-sharing strategy. Similarly, members of the Senate majority party are chosen to chair all committees. However, the nature of the Senate requires that the majority leaders of committees work with the ranking member of the minority party to accomplish the committee’s goals.
(A presidential veto prevents the legislation from taking effect.) If the president approves the bill, it’s signed into law. If the president rejects the bill, it’s returned to Congress with an explanation for the veto. A bill can be introduced by a representative or a senator; that person becomes the bill’s sponsor (note that bills can have multiple sponsors). After meeting in small groups to discuss the bill’s merits, representatives or senators assign the bill to a committee for further research, discussion, and potential amendments.
Majority and minority leaders represent their respective parties on the House floor. Whips assist leadership in managing their party's legislative program on the House floor. A party caucus or conference is the name given to a meeting of or organization of all party members in the House. When the bill comes up for consideration, the House has a very structured debate process. Each member who wishes to speak only has a few minutes, and the number and kind of amendments are usually limited. In the Senate, debate on most bills is unlimited — Senators may speak to issues other than the bill under consideration during their speeches, and any amendment can be introduced.
Through this, Congress can respond to changing circumstances and to address issues of national importance, such as protecting the environment, promoting economic growth, and addressing social issues such as healthcare, education, and civil rights. The Senate is smaller and Senators, therefore can become more prominent. Senators have been serious Presidential or Vice-Presidential candidates. House members become Senators, but virtually never the other way around. The Constitution gave exclusive roles to the Senate which may be seen as higher status, such as conducting impeachment trials, ratifying treaties and agreeing to executive and judicial appointments.

No comments:
Post a Comment